Definition: LT lines are low voltage based lines used for distributing electricity at low levels such as up to 1 kV (1000V) to residential, small industrial, and commercial consumers.
Key Characteristics:
● Operates at voltages like 230V (single-phase) and 415V (three-phase).
● Used for local electricity distribution.
● Commonly seen in urban and rural areas supplying households, shops, and small businesses.
● Often consists of overhead wires or underground cables.
Applications:
● Domestic power supply.
● Street lighting.
● Small-scale industrial applications.
What Jera Line provides for LT line?
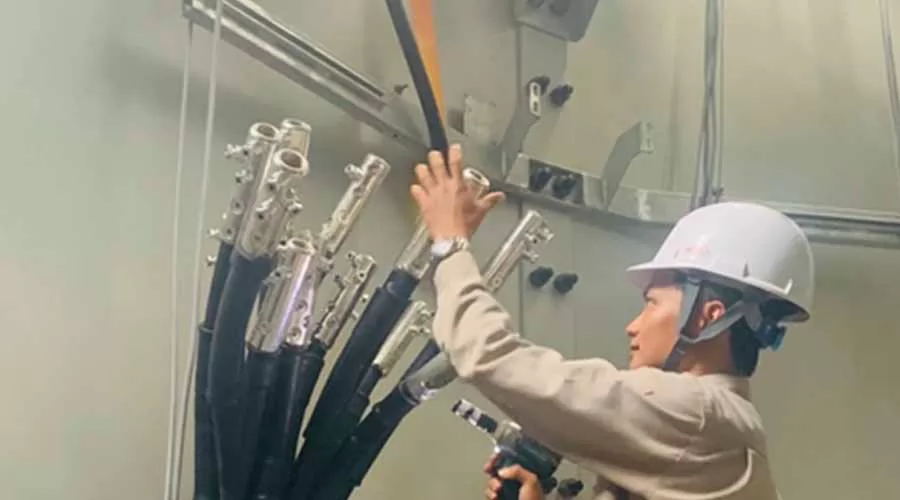
● Overhead Anchor & Suspension: Products like helical wire dead end guy grips and tension clamps to securely anchor and suspend overhead cables.
● Insulation Piercing Connectors: Connectors that allow for quick and reliable connections for bare and insulated cables.
● Overvoltage Protection & Current Limitation: Devices such as surge arresters and overvoltage protection holders to safeguard the electrical system.
● Termination & Connection: Pre-insulated cable sleeves and lugs for secure termination and connection of cables.
● Underground & Indoor Connection & Termination: Shear head bolted mechanical cable lugs and connectors for low voltage lines.
Definition: HT lines carry electricity at higher voltage levels, typically ranging from 11 kV to 33 kV. These lines are used to supply power to industrial facilities and large commercial establishments.
Key Characteristics:
● Transmits electricity over medium distances.
● Used for large consumers like factories, hospitals, and large buildings.
● Reduces transmission losses compared to LT lines.
● Requires step-down transformers at the consumer end to lower voltage for usage.
Applications:
● Large industrial plants.
● Commercial complexes
● Large-scale agricultural operations.
What Jera Line provides for HT line?
● Insulation piercing connectors for MV : It designed for medium voltage ABC cables up to 36KV.
● Mechanical cable lug for MV: It used in up to 36KV power distribution system.
Definition: Transmission lines are responsible for carrying electricity over long distances from power generation plants to substations before distribution. These operate at extra-high voltage (EHV) levels, typically 66 kV and above, reaching up to 765 kV.
Key Characteristics:
● Designed for long-distance bulk power transmission.
● Operates at extra-high voltage (EHV) to reduce power losses.
● Constructed using high-strength conductors and large steel towers.
● Electricity is stepped up to high voltage at the generation source and stepped down at substations before distribution.
Types of Transmission Lines:
● Primary Transmission: 132 kV and above, transferring power between generation stations and substations.
● Secondary Transmission: 66 kV to 132 kV, distributing power between substations before final delivery.
Applications:
● Nationwide power distribution.
● Cross-border power transfer.
● Renewable energy integration from remote generation sites.

|
Feature |
LT Line (Low Tension) |
HT Line (High Tension) |
Transmission Line |
|
Voltage Range |
Up to 1 kV |
11 kV - 33 kV |
66 kV and above |
|
Purpose |
Local distribution |
Industrial and commercial power supply |
Long-distance transmission |
|
Losses |
High |
Moderate |
Low due to high voltage |
|
Common Use |
Homes, shops, small industries |
Large industries, commercial buildings |
Power plants to substations |
|
Infrastructure |
Poles, cables, underground |
High-capacity cables, towers |
Steel lattice towers, large conductors |
Understanding Low Tension (LT), High Tension (HT), and Transmission lines is essential for optimal operation of the electric grid system. You can get the solution for LT line connection needs from Jera Line, and we are working on the solutions required for HT line connections.
If you need further assistance or have any questions, feel free to reach out!